I am a Linux beginner/amateur and I have sort of had enough of copy and pasting commands I find on the internet without having a good understanding of how they actually work.
I guess my end goal is to be able to comfortably install and use arch Linux with my own customization’s and be able to fix it when things go wrong.
What tips/ideas do you have for getting better at navigating the terminal, and getting a better understanding of how the os works. What is a good roadmap to follow? And how did you, advanced Linux user, get to the stage your at now?
Edit: my current distro is bazzite just in case you were interested and thanks for all the replies you are all really helpful.
Command line cheat sheet (with bonus vim controls):
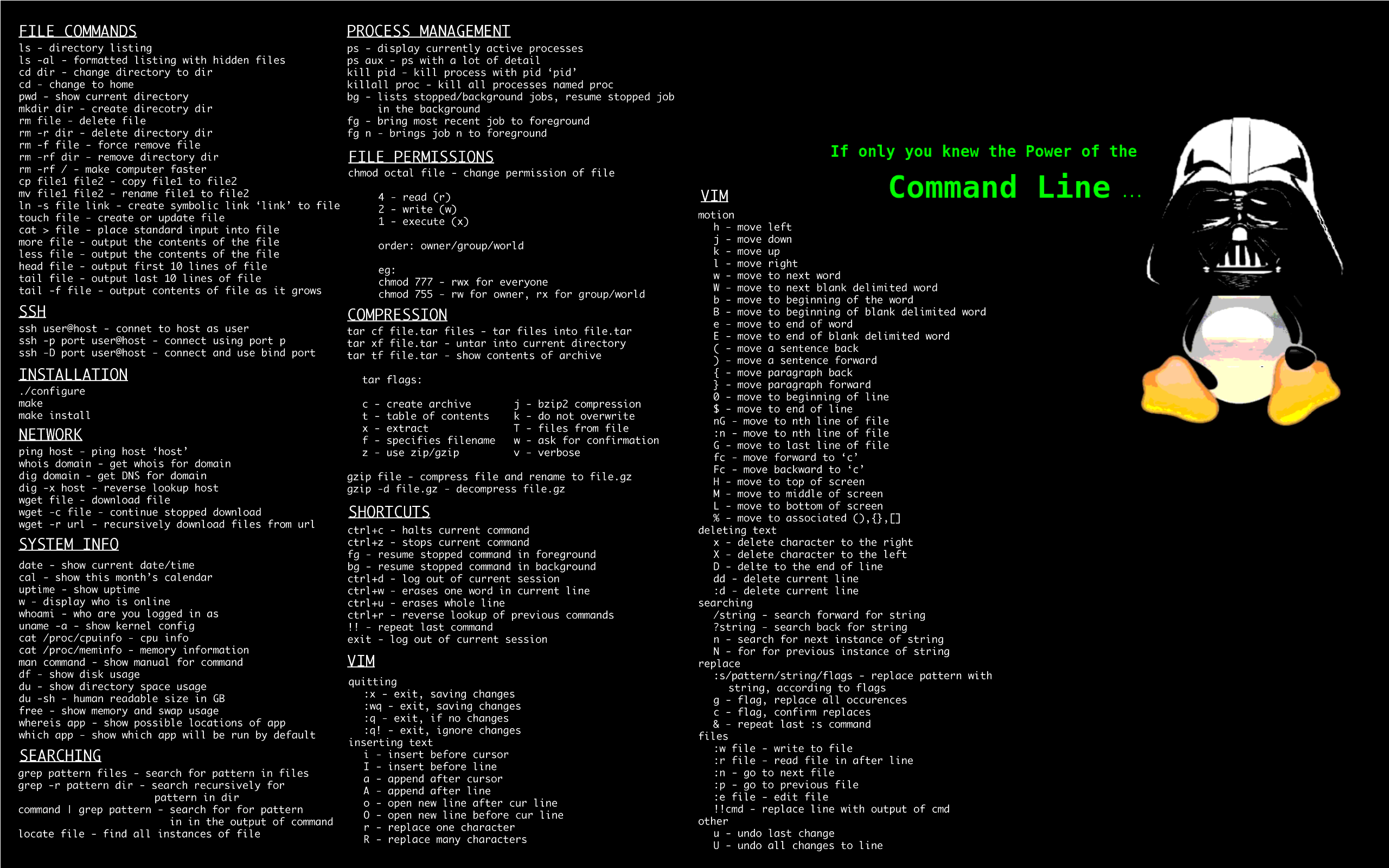
That’s kind of awesome, thanks!
And stop copy/pasting them. Type them out so you get used to them. It gets quicker the more you do it.
rm -rf /
make computer faster(͠≖ ͜ʖ͠≖)
Wait I did this to my main drive everything went black is this suposed to happen? will it start working again?
in case you aren’t joking, rm -rf / (albiet with a warning now) will delete allll the files on your system, so everything going black is the expected result.
rm is remove, the - is to indicate that you want to pass arguments, and r&f are recursive (delete stuff in the folders in this folder) and force (don’t ask for confirmation). The slash afterwards designates the root folder, the folder with everything in it.
So “rm -rf /” means “remove, recursively and forcefully, everything in the / directory”
@Blisterexe @pineapple , after making a snapshot of VM. Sometimes, I do it just for fun and then roll back to the snapshot. Fun times.
it is a fun command to see happen, i agree
It sounds a bit nerdy, but dedicate some time just to learning a specific command once in a while. Start with something straightforward like
ls. Read through themanpages and try out all the different options for it. After a while, you’ll master quite a few commands and will be able to string them together to perform more complex tasks. It’s definitely easier learning the system piece by piece like this. I used to learn by just jumping right in to a complex task, but I ended up with just a superficial understanding most of the time. Now days I try to be more deliberate about reading all the documentation and actually learning the tool/command/etc.Also, Arch has the
archinstallscript that greatly simplifies the install process if you need it. You’ll definitely learn more doing it manually though. I’ve been using Arch as my daily driver for a year now and I love it.The tldr cli (tldr.sh) is a great way to get familiar with options of differ programs.
Very useful, even for someone who has been using Linux for many years. Sometimes you just forget or need that tool you rarely use.
tldrcan be much handier than parsing a man page when you’re in a pinch.I use the tealdeer implementation, but any is fine really.
- You can always use
man commandand just read through it. If you want less text, usecurl cheat.sh/command(learn how to use aliases) or the toolstldrandcheat - Install the fish shell, it makes using the terminal waaay easier, out of the box.
- Install Alpaca flatpak, and use tinyllama or bigger LLM models. Tinyllama is already very sufficient at explaining linux commands and more, and runs fine on my reasonably powerful and modern laptop. Other models may be slow as fuck.
- Use the terminal only. Log out, Ctrl+Alt+F2 and login, then use some tools.
$pwd cd echo ls cat nano less more chmod chown #your package manager lsblk dd #be careful! udisksctl lsusb lspci curl wget ...Note: use the man for these tools and often multiple tools do the same thing
- There is this online terminal game/quiz but I cant find its name.
Install the fish shell, it makes using the terminal waaay easier, out of the box.
Not a good idea if the goal is to learn more about Linux. Fish is not compatible to and is different to Bash in some ways, that it would be hard once not using Fish. Also getting help or sharing scripts with others will be problematic, when having a problem and researching it. For someone coming in to Linux and wanting to learn about it, I highly recommend to learn about Bash first and use it at least for months before even thinking about a custom shell. I used Fish too (and I miss some features), so its not like I wouldn’t know what it is.
Install Alpaca flatpak, and use tinyllama or bigger LLM models.
Alpaca is nice. GPT4All is also another one (and one that I prefer). Either way, both are good. But again like previous point, I do not recommend to install and use Ai modesl (LLMs) to learn about Linux and to get used to it. Especially the smaller models often hallucinate and lie with false claims. If you don’t know it better and are currently learning, this could be a problem. I highly discourage from installing and learning with an Ai model alongside when you are new to a topic like Linux. Its also not like there wouldn’t be enough good material out there anyway.
Fish is just a shell, you can still write and execute bash scripts
Fish is rewritten in Rust btw
Also the syntax is waay better, it should totally replace bash
My point is that Fish is not standard Linux tool. If the goal is to learn more about Linux, it makes more sense to learn about Bash first. I’m not against Fish. For a newcomer its just confusing when researching stuff or reading others scripts in Bash and constantly think about the differences in Bash and Fish. Or if you want to share a script with someone who does not have Fish. I’m not saying Fish is bad or anything like that. I’m just saying for a newcomer its not a good idea to ignore Bash and learn Fish first for someone who is interested into learning more about Linux and its eco system. Fish itself has the better language, no doubt about it and is actually better than Bash. But the quality is not my main concern in the reply.
As I said. Fish can just be a shell. I only write bash scripts. All bash scripts have
at the beginning so it doesnt matter.I dont know about fish errors. If something doesnt work, I enter
bashand then run it again. I enterexitwhen I am done.That does happen but the workaround is easy
Apart from that, instant suggestions, history, arguments and available commands already help a lot.
Fish can just be a shell. I only write bash scripts.
That’s the exact problem. You deal with two languages. I did that too BTW. Now for someone who is experienced, its fine. But for someone who just started learning about Linux and scripting, its not ideal, as it adds unnecessary complications and friction for a learning process that is already complicated. Because learning Bash is a must do in my opinion. Regardless what custom shell you use.
After that learning process and getting familiar, one still can decide to use Fish as the interactive shell. But that’s AFTER the initial learning process of the basics of Linux.
- You can always use
Install TLDR pages from your package manager to get easy access to the most useful information
To be honest I’ve been using Linux for years and I still paste commands all the time. The only difference is that now when I am trouble shooting I know what command I need just not the options and how to use it
What tips/ideas do you have for getting better at navigating the terminal, and getting a better understanding of how the os works
Running an OS as a virtual is liberating. Dive in, make mistakes, fix them (or not and have to reinstall or redo from the last save). No real consequences for exploring.
More than anything, what leveled up my Linux knowledge was switching to Gentoo back while I was in college.
Before that, I used SuSE, and I switched specifically because I felt like I wasn’t learning anything really about Linux just by using point-and-click tools like YAST.
I’ve used Arch for the last… 7-ish years? (Though now I’m basically in the process of switching back to Gentoo. In terms of learning Linux, Arch is… close to as good as Gentoo for that purpose. Not quite as good, but pretty close.)
As for the best approach for learning, though, you know how they say the best way to learn a language is “immersion”? As in, to move to where they speak the language. In the same way, if what you’re going for is to learn, just take a dive. Install Arch over top of your current OS and don’t look back. Just commit to it.
Also, use the most minimal stuff you can. Skip KDE and use dwm. Skip the login manager and start your GUI from the command line. Don’t install a file manager and instead use Bash directly. (It’s more than capable.) Don’t install anything you can do instead with a Bash one-liner or a small Bash script. If after you’ve gotten pretty used to minimal stuff you still want something that the heavier alternatives offer, you can of course switch, but if your aim is to learn, avoid using the kind of stuff that tries to be “user friendly” by hiding all the internal implementation details from you. (Instead use the stuff that is user friendly by virtue of having so few moving parts that understanding how it works under-the-hood is trivial.)
And, don’t settle for “it’s fucked beyond repair.” If it’s fucked, google your ass off. If that doesn’t work, ask on the official Arch forums or here or wherever. (Don’t worry, they don’t bite.)
Is bash ultimately better than dolphin or another file manager? I always thought that it just seamed slow having to read things out with no icons and having to type the filename instead of double clicking. And I have been avoiding installing applications through terminal because I can’t find how to properly uninstall them including all data (the fedora software center does this really easily) I have also had some trouble going further back that my user folder in the terminal I still havn’t figured out how to do that. Lastly what are some “user friendly by virtiue of having few moving parts” distro’s that you recommend?
having to type the filename instead of double clicking.
Google “tab completion”
Is bash ultimately better than dolphin or another file manager?
-
Yes. (Disclaimer, some statements contain opinion.)
-
OP was specifically asking how to learn more about Linux. And it’s nearly unquestionable that OP is going to learn more about how Linux works if they use the lower-level tools rather than take-you-by-the-hand point-and-click-adventure programs your grandmother could probably figure out.
I always thought that it just seamed slow having to read things out with no icons and having to type the filename instead of double clicking.
So, again, this is just me spouting my own preferences here, but I don’t often touch the mouse. Moving my hand from keyboard to mouse takes time. I can use a keyboard shortcut to open a terminal, cd into the proper directory (using tab complete and
set -o vito make things quicker still), and start dealing with files much quicker than I could navigate a menu to get to, say, Dolphin, wait for it to load (if you use a minimal terminal, it should load basically instantaneously), and then start navigating.And I have been avoiding installing applications through terminal because I can’t find how to properly uninstall them including all data (the fedora software center does this really easily)
Not sure I can help you there. I’ve never used Fedora. I used CentOS once for a short time, but it was a long time ago and I basically don’t remember it at all.
I have also had some trouble going further back that my user folder in the terminal I still havn’t figured out how to do that.
Like, to the parent directory of your home directory?
cd ..should always go to the parent directory of your current working directory. (/is its own parent, I believe, so you can’t go any further up the chain than that.)Lastly what are some “user friendly by virtiue of having few moving parts” distro’s that you recommend?
Gentoo and Arch. I’ve never used Void, but it sounds to me like Void is very minimal (has few moving parts) while also being much less of a learning curve than Gentoo and Arch.
When I say “few moving parts”, I mean, roughly speaking, fewer lines of source code. KDE (just for instance) is a huge beast. It tries to accomplish user friendliness by adding layers upon layers of abstraction, in the process obscuring what’s really going on at lower levels from the user. It… doesn’t really work. What it gains you in reduced learning curve becomes an obstacle the moment something goes wrong or you want to peek under the hood. Ubuntu (just as another example) installs tons of stuff to try to shield you from the nitty gritty details. But again, that causes more problems than it solves unless you’re dead set against ever looking under the hood for any reason.
The term “user friendly” tends to mean “my grandmother can use it without having to learn anything in the process.” In the comment about “user friendly by virtiue of having few moving parts”, I didn’t mean “user friendly” in the same sense. I don’t think “user friendly” in the more common sense id mutually exclusive with “fewer moving parts.” At least not in theory. But in practice, that does seem to be the trend.
OP was specifically asking how to learn more about Linux. And it’s nearly unquestionable that OP is going to learn more about how Linux works if they use the lower-level tools rather than take-you-by-the-hand point-and-click-adventure programs your grandmother could probably figure out.
Yes I am op.
and thanks for the reply. So I guess I should just skip anything with a desktop environment like manjaro and just figure out how to install bare arch?
Like, to the parent directory of your home directory? cd … should always go to the parent directory of your current working directory. (/ is its own parent, I believe, so you can’t go any further up the chain than that.)
Yes
cd ..was what I was looking for thanks!Yes I am op.
Ha! That’s what I get for posting on Lemmy at 2:00 am. Lol.
So I guess I should just skip anything with a desktop environment like manjaro and just figure out how to install bare arch?
You can certainly start with a bare Arch install and install on top of that a graphical environment. (Without a graphical environment, you wouldn’t be able to run a full-featured browser like Firefox or Chromium or whatever, for instance. I’d think if you intend to use this system as your daily driver – and I’d recommend you do for learning sake – you’ll probably want a graphical environment.) But, yeah. I’d say Arch isn’t that unapproachable to install without going the Manjaro route or the “archinstaller” route.
With Arch, everything’s just packages. The difference between non-graphical Arch and graphical Arch is just that non-graphical Arch doesn’t have any graphical system packages installed.
Now, I keep talking about “graphical systems”. There are two ways to go with that. There is X11 which is mature but a bit dated. And there’s Wayland which is the new hotness but support for it is still a bit lacking, so some features like screen grab may not be supported by all programs and some programs won’t work as straightforwardly on Wayland. (Basically, any time a program grabs an image or video of any portion of the screen of your graphical environment, that uses the “screen grab” API. Wayland does that differently than X11, so a lot of programs aren’t updated to use Wayland’s way yet.)
I guess I’d probably lean toward recommending X11 at this point. I personally use a Wayland compositor (Sway, specifically), but I don’t think running Wayland is going to teach you much that X11 won’t, and running Wayland at this point is likely to introduce frustrating wrinkles. If after you have your Linux “sea legs” you want to try switching, that’s always an option as well.
As for minimal X11 environments, first off, I’d say avoid things that describe themselves as “desktop environments”. They’re likely to hide details from you. Prefer “window managers.” Tiling window managers tend to be more minimal, but if you want to go with a more draggy-droppy, mouse-driven window manager that feels more like what you’re probably used to (but also doesn’t hide details), I’d recommend IceWM.
And, finally, as far as a “bare Arch install”, the place to start is the install guide on the Arch Wiki. It goes step-by-step on how to do things. And take the time to understand the commands you’re running as you’re running them. There are a lot of links in the install guide to more in-depth articles. For instance, the “partitioning” section links to an article called “partitions” that goes in depth on what a “partition” even is.
There’s a lot to learn, but it also pays off. Both in terms of just having the power to do the stuff you want with your own systems and in terms of benefits to your career. And it’s just plain fun!
Thanks, I guess I will go with x11 with a tiling window manager, I’ve had enough of windows being on top of each other and I like the idea of using my mouse the least amount possible. One last question most apps and packages don’t support pacman sometimes the only option is to install with apt and you download a .dev file is there a way to get around this?
Great question!
So, first off, if I knew what app(s) specifically you have in mind, that’d help me answer better, but in general:
- First off, I’ll say it’s mostly less that they support pacman than that Arch supports them. There may be some exceptions, but it’s usually Arch developers building the pacman packages rather than the author of the software in question. Even when it’s a proprietary application, it’s usually bundled into a packman package (or at least a PKGBUILD for it lives on AUR, but we’ll get to that) by one of the Arch developers or other volunteers.
- Your first option for software that isn’t in the official Arch repositories is AUR. It’s for packages that aren’t as officially supported as those in the official Arch repositories. Anything in AUR, you’ll have to build the package itself (which usually involves compiling, unless it builds the package from an already-compiled binary), but the process is usually pretty straightforward. (Download and unzip the tarball from AUR somewhere, cd into the directory, and then
makepkg -sf && sudo pacman -U <something>.tar.xz. You can also get some helper scripts that do some of those steps for you for convenience. Definitely worth having the experience of doing it manually a few times first, though, I’d say.) Even if the only way to get the software in question from the publisher is in .deb form, you may still find a package on AUR that will unpackage the .deb and package the result up into an Arch package. - You can run the software in an isolated way. There are snap packages and flatpacks, but… well, there are good reasons why they get a bad rap. Lol. Another option is to build an Ubuntu chroot in which to install the package in there. The cleanest and most straightforward option for running software isolated like this is probably Docker. (Running graphical apps in Docker can definitely be done, though it is a little tricky.)
- You can grab the software in question and install it manually somewhere in your home directory. Somewhere like
$HOME/install/<softwarename>. This can work even if the software is only available as a .deb file. You can just extract the .deb without installing it with the commandar x <blah>.deband atar -xf data.tar.gzand then put the files from within that .deb file where you want them. - There are some other options that I’ve never tried (and only learned of just now by googling) that… aren’t recommended. Here’s a link for reference, but to somewhat explain the problems that those approaches there can cause, when you install a package from any particular package manager, the package manager installs dependencies. (Typically those dependencies are shared libraries. Think ".dll"s.) And those dependencies live in specific places. But if, say, you had pacman and apt-get installed on the same system and install the same dependency (including if that dependency is installed automatically as part of installing something else) via both package managers, it’s likely to get one version of the dependency from one package manager and another from the other. Either one package manager is going to error out (“these files already exist in the filesystem, I think something’s wrong that a human should fix”) or overwrite files potentially breaking things. (Now, all that said, I know that pacman is actually in the official Ubuntu repositories and can be installed on Ubuntu alongside apt get. I have to admit I don’t know if and if so how it goes about avoiding problems if both are installed. Maybe it’s not a good idea to install pacman on Ubuntu for the same reason. Who knows!)
- So, there is also the option to write your own PKGBUILD. (A “PKGBUILD” is a script that tells your Arch system how to build a Pacman package. They’re what you download from AUR when you want to build/install something from AUR. A couple of reference links.) It does require doing a little Bash programming, but It’s not as hard as it sounds. (And it’s easier than building Ubuntu packages.) I’ll talk about what to do if you truly can’t get the package in question anyhow except in .deb form. But first, if you can get the source code, you can typically grab a PKGBUILD from the official Arch repositories or from AUR that installs something “similar” to what you’re wanting to install and modify it. (Like, for a simple example, if you’re trying to install something written in C, you can look for a PKGBUILD for something written in C that would probably have similar dependencies.) If you can’t get the source code but can get a compiled distribution of the software in question, you can still write a PKGBUILD, and you’ll probably be able to find some PKGBUILDs to start from that would be pretty similar to what you need.
- If you truly can’t get the software in question except in .deb form and you want to write a PKGBUILD for it, that can be done. It just involves writing a PKGBUILD that extracts the files from the .deb file and then packages them back up into an Arch package. I’ve done this before and I have a funny personal story about that. More info here in an answer to another question in this same Lemmy community.
Just in case it’s useful to you, I’ll share the PKGBUILD I wrote for converting the Ubuntu kernel into an Arch package. It demonstrates how you’d go about extracting files from a .deb file in order to build them into an Arch package.
pkgname='linux-ubuntu' pkgdesc='The Ubuntu kernel, modules, and headers' pkgver='5.15.0' _pkgver="$(cut '-d.' -f 1,2 <<< "${pkgver}")" _firmware_ver='1.187.29' _suffix_ver='20.04.2' pkgrel='25' arch=('x86_64') options=('!strip') url='http://ubuntu.com/' source=( 'http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/l/linux-firmware/linux-firmware_'"${_firmware_ver}"'_all.deb' 'http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/l/linux-hwe-'"${_pkgver}"'/linux-headers-'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'-generic_'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'.'"${pkgrel}"'~'"${_suffix_ver}"'_amd64.deb' 'http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/l/linux-hwe-'"${_pkgver}"'/linux-hwe-'"${_pkgver}"'-headers-'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'_'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'.'"${pkgrel}"'~'"${_suffix_ver}"'_all.deb' 'http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/l/linux-signed-hwe-'"${_pkgver}"'/linux-image-'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'-generic_'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'.'"${pkgrel}"'~'"${_suffix_ver}"'_amd64.deb' 'http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/l/linux-hwe-'"${_pkgver}"'/linux-modules-'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'-generic_'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'.'"${pkgrel}"'~'"${_suffix_ver}"'_amd64.deb' 'http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/pool/main/l/linux-hwe-'"${_pkgver}"'/linux-modules-extra-'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'-generic_'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'.'"${pkgrel}"'~'"${_suffix_ver}"'_amd64.deb' 'linux.preset' ) noextract=( 'linux-firmware_'"${_firmware_ver}"'_all.deb' 'linux-headers-'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'-generic_'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'.'"${pkgrel}"'~'"${_suffix_ver}"'_amd64.deb' 'linux-hwe-'"${_pkgver}"'-headers-'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'_'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'.'"${pkgrel}"'~'"${_suffix_ver}"'_all.deb' 'linux-image-'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'-generic_'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'.'"${pkgrel}"'~'"${_suffix_ver}"'_amd64.deb' 'linux-modules-'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'-generic_'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'.'"${pkgrel}"'~'"${_suffix_ver}"'_amd64.deb' 'linux-modules-extra-'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'-generic_'"${pkgver}"'-'"${pkgrel}"'.'"${pkgrel}"'~'"${_suffix_ver}"'_amd64.deb' ) sha256sums=( '22697f12ade7e6d6a2dd9ac956f594a3f5e2697ada3a29916fee465cc83a34a1' '595794e8ad28ed130af60e6ec8699313e1935ae70f7530a00b06dff67fb4d40e' '22dbdc1895f91d3ad9d4c5b153352f1cc8359291dba6ea1a0e683cc6871b0f58' '5705cefab39dd5512bcc515918d09153715c7bb365d6bc29cc9b0580e5723eef' '3d207388812e957447162c067fb637b4d06eccb4f303b801e8402046a7d3cf48' '2f1214dbb04cb47ce8d096bff969fca9c78c26ec21a395c12922eca43cc18e26' '75d7d4b94156b3ba705a72ebbb91e84c8d519acf1faec852a74ade2accc7b0ea' ) package() { for f in "${noextract[@]}" ; do ar x "${f}" tar -xf "data.tar.xz" -C "${pkgdir}" done rm -r "${pkgdir}"'/usr/share' rm -r "${pkgdir}"'/usr/lib' mv "${pkgdir}"'/lib' "${pkgdir}"'/usr' install -Dm644 'linux.preset' "${pkgdir}"'/etc/mkinitcpio.d/linux.preset' }(I omitted the
linux.presetfile. It’s just in the same directory with the PKGBUILD and it gets bundled into the Arch package. But it’s not really important for what you’re doing unless you’re trying to install a different kernel than the official Arch kernel on an Arch system.)The part that extracts the files from the .deb packages is the
ar xcommand and thetar -xfcommand. Thepackage()function there is what decides exactly what files will be in the Arch package and where. Andmakepkgbuilds the package archive after runningpackage().That covers all the options for installing software not in the Arch repos that I can think of.
Thanks for the reply and I will definitely use some of the less advanced options for now.
-
thanks for the required motivation! i started to settle, i will try arch today after i am done with my exams.
If you want to get better at Linux terminal and standard unix commands I would try https://overthewire.org/wargames/bandit/
It’s an interactive tutorial which will help build basic skills. There are a million guides and walkthroughs for this, but I would try each level on your own first before you look at a guide.
For getting better at terminal I would suggest looking into alternative shells. Bash is fine, but it’s not exactly user friendly by default. Something with more robust auto completion like zsh or saner defaults like fish could make the learning experience easier. You can always come back to bash later.
For understanding how the OS works I would start by reading about the file system layout, then look into the init process.
I got to the point I am at through a series of projects of increasing complexity. First I ran a web server on my machine to copy files over the network. Then I used a spare PC to make a simple SMB server. Later I made it into a HTPC pirate box, for streaming stuff downloaded off Usenet to my Xbox. At some point I ran a minecraft server (before docker came along and trivialized this), and got into a bunch of sysadmin and programming stuff and that’s pretty much it.
Just out of curiosity, do bash script work in zsh? Or are they totally different things and are not cross compatible?
Depends on what it is. If it’s meant to be mainly used in the shell I will usually use whatever language the shell uses. Anything that’s run automatically usually gets done in bash for compatibility, and stuff more complicated than a few loops and some piping gets done in something easier to work with like python.
Start running servers if you haven’t already. Use an old computer, or an SBC or VPS and setup some Linux servers. There’s lots of different ways to do it, so mess around and break shit over and over. You can’t help but learn that way, though I would highly suggest you take notes/documentation. This is a habit I’m trying to develop after too long :)
My advice would be look up The Missing Semester it’s a free online MIT course on how to use the terminal and it will govern you a better understanding of how to use it and Linux more generally. Really helpful to find your way around and give you an intuitive sense of what you’re trying to achieve.
Then beyond that installing arch is easy with archinstall but it’s probably more helpful to learn about the components of desktop Linux and what they do so that you actually know what you’re doing.
start from
man manand learn to use man pages. Get used to lookup man pages for any topic before checking on the internetThis is it. You’re likely not going to get away from needing help from time to time. Instead of focusing on trying to know everything, focus on knowing where to find what you need. It’ll click from there with time.
I still find Tealdeer useful even now, it helps me get working with commands I know little about, more so than a manpage
Just install Arch, when You follow wiki it’s not that hard. if You will make mistakes during the process, You will gain better understanding of how things works while fixing errors.
This. The arch wiki is a treasure trove of information. The more you do, the more you’ll learn.
Also, don’t blindly copy paste configs for editors or window managers. Just slowly build them up based on your own use. It’ll be painful initially but worthwhile in the long run
I think I will try something like manjaro first see what it’s like and then move onto arch.
That was exactly how I did it some years ago. After 4 or 5 times fixing the X-server after an update (thanks nVidia!) I switched over to Arch. Installed Arch following the Wiki for about 2 hours… failed and started the process of installation again (in about 1.5 hours :P) and succeeded. By failing and trying again I’ve learned a ton. My advise for less frustration: go with Team Red. In my experience AMD graphics cards are much more linux-friendly.
see this post for my experience with amd lol.
+1. and yes use the wiki not the install script.
I think theres value to anyone with a genuine interest if they just have a go at an archinstall - I think they can setup most things of interest in a Qemu(vm), or a spare partition, or even a usb or something. Theres nothing to lose but time. I’d recommend the user knows enough about their disk setup and their incumbent boot manager so as not to screw up their main os. Though i’m very tempted to say that’s a rite of passage.
Of course everyone already has a regular backup(s) which contains some sort of list or script for all the software, configs and tweaks they normally do. If not - well another rite of passage.
Certainly a worthwhile endeavour. But I’d recommend doing it in a VM or a secondary machine before jumping right in on your main computer.















